Discover Premium Ceramic Products | Durability & Elegance United | Advanced Ceramics
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description
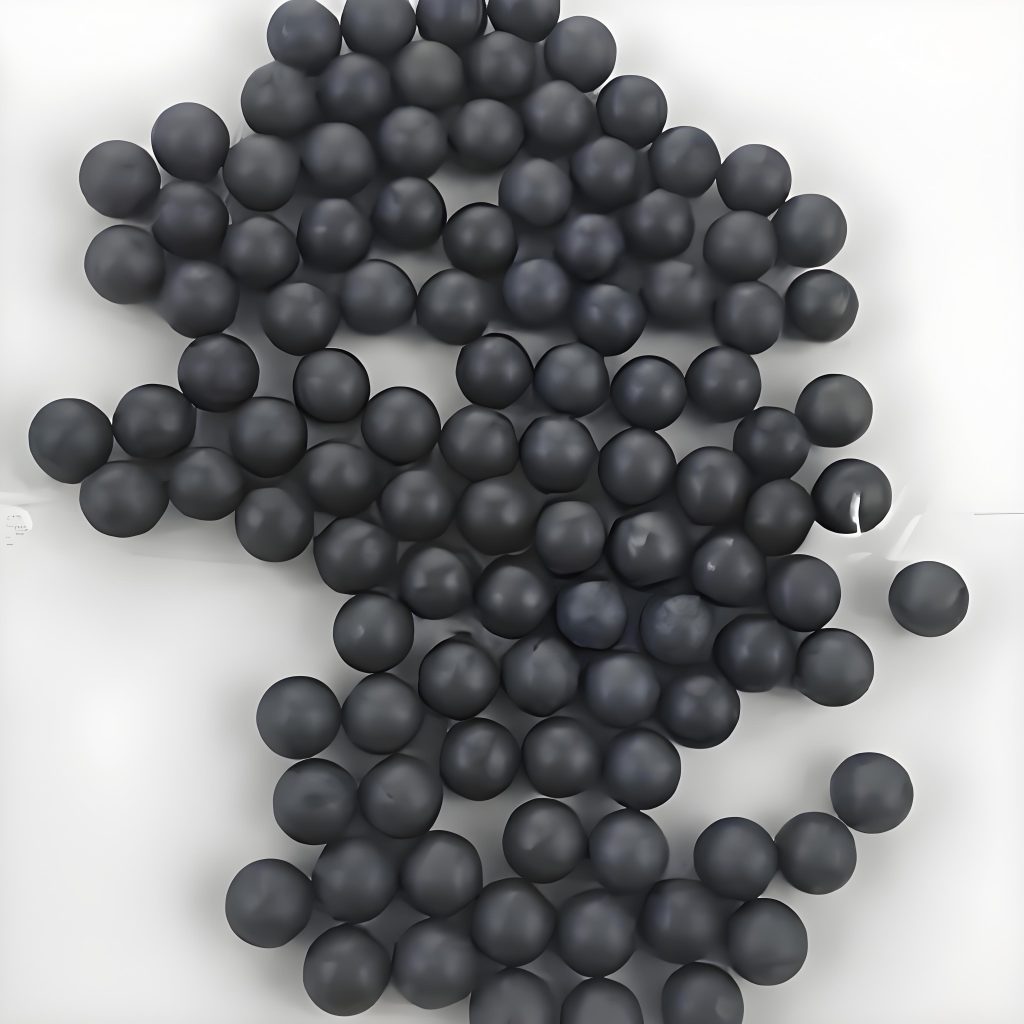
Overview of Boron Carbide B4C Balls:
Boron carbide balls are spherical structures made of boron carbide. Boron carbide material is famous for its extremely high hardness, high melting point, excellent wear resistance and chemical stability. Due to limitations in hardness, temperature resistance or chemical reactivity, these balls can be used in environments where traditional materials are not competent.
Features of Boron Carbide B4C Balls:
Extremely high hardness: The Vickers hardness of boron carbide balls is about 35 GPa, which has unparalleled wear resistance.
High melting point: The melting point of boron carbide balls is about 2450°C (4442°F), so they can withstand extremely high temperatures without significant degradation.
Low density: Although boron carbide has extremely high hardness, its density is relatively low, approximately 2.52 g/cm³, which helps achieve a lightweight design.
Chemical stability: High resistance to most acids and bases, making it suitable for use in corrosive environments.
Thermal conductivity: Moderate thermal conductivity can achieve efficient heat dissipation.
Electrical insulation: It can be used as an effective electrical insulator and is suitable for electronic applications.
Neutron absorption: The high neutron absorption cross-section makes boron carbide balls of great value in nuclear applications.
Brittle: Although boron carbide is extremely hard, it is also brittle, which may limit its application in situations involving high-impact loads.
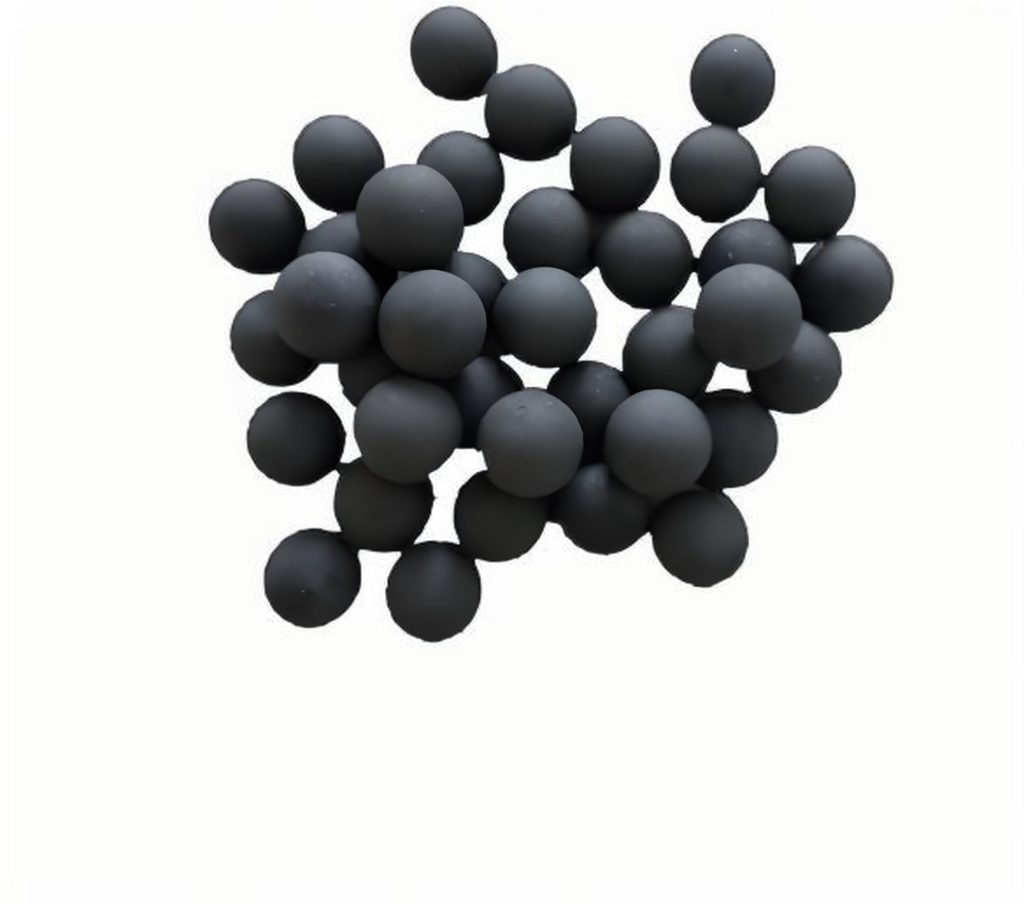

Boron Carbide B4C Balls
Specifications of Boron Carbide B4C Balls:
| Property | Specification |
| Chemical Formula | B₄C |
| Hardness (Vickers) | ~35 GPa |
| Density | 2.52 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 2450°C (4442°F) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 27-129 W/m·K (depending on purity and orientation) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 6.5 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ |
| Electrical Resistivity | High (acts as an electrical insulator) |
| Compressive Strength | > 3.5 GPa |
| Tensile Strength | Relatively low due to brittleness |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 460-500 GPa |
| Fracture Toughness | Low (~3 MPa·m^(1/2)) |
| Chemical Stability | Highly resistant to most acids, alkalis, and molten salts |
| Neutron Absorption Cross Section | High (~760 barns for natural boron) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in most environments |
| Acoustic Properties | Good sound damping characteristics |
| Biocompatibility | Generally considered biocompatible |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic; long service life reduces replacement frequency |
| Manufacturing Process | Hot isostatic pressing (HIP), sintering, reaction bonding, machining, polishing |
| Typical Dimensions | Diameter: varies by application (common sizes include 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm, etc.) |
| Surface Finish | Can be polished to high precision (Ra < 0.1 μm) |
| Sphericity | High precision, typically within ±0.002 mm |
| Roundness | High roundness, typically within ±0.002 mm |
| Weight Tolerance | Typically within ±0.5% |
Applications of Boron Carbide B4C Balls:
Bearing: Industrial bearings: Used for mechanical bearings that require high wear resistance and durability, such as the mining, construction and aerospace industries.
Precision bearings: Ideal for precision applications with minimum wear and long service life.
Ball valve: used for ball valves exposed to severe conditions such as high pressure, high temperature and corrosive media.
Grinding and polishing: Used as a grinding medium in grinding wheels and polishing agents for precision machining operations.
Nuclear Industry: Control rod components: Used in nuclear reactor control rods to absorb neutrons and ensure safe and controlled operation. Military and defense
Armor components: Integrated into personal and vehicle armor systems for ballistic protection.
Medical equipment Dental instruments: Used for dental instruments that require durability and non-corrosion.
Implants: Due to their biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, they can be used in certain types of implants.

Company Profile
Advanced Ceramics founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials and products. Since its establishment in 2012, the company has been committed to providing customers with the best products and services, and has become a leader in the industry through continuous technological innovation and strict quality management.
Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. Please feel free to contact us.(nanotrun@yahoo.com)
Payment Methods
T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.
Shipment Methods
By air, by sea, by express, as customers request.

FAQs of Boron Carbide B4C Balls
1.How do boron carbide balls compare to steel balls?
A: Compared to steel balls, boron carbide balls offer superior hardness and wear resistance, making them more durable in grinding environments. However, they are also more brittle and can be more expensive due to the complex manufacturing process.
2.Can boron carbide balls withstand high temperatures?
Answer: Yes, boron carbide balls have a very high melting point and can maintain their structural integrity at very high temperatures, making them suitable for applications involving extreme heat.
3.Are Boron Carbide balls easy to machine?
A: Due to their extreme hardness, machining boron carbide balls can be challenging. Specialized tools and techniques such as diamond grinding or laser cutting are often required. This can increase production costs and complexity.
4. Can boron carbide balls be recycled?
A: Recycling boron carbide balls is challenging due to their hardness and the difficulty of breaking down the material. However, its long service life reduces the frequency of replacement and indirectly contributes to environmental sustainability.
REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS

Sandblasting Grit/Sand Blast Boron Carbide B4c Nozzle

99% Boron Carbide B4c Sand Boron Carbide Granulation Powder B4c Nano Boron Carbide Powder Coating
SW40 Body Protection Flat/Curved Boron Carbide Hexagonal Ceramic Plate B4C SIC Tiles

B4C Boron Carbide Powder 30um F325 for Making Boron Carbide Ceramic Vest

Light Weight Boron Carbide B4C Ceramic Hexagon Tiles For Bulletproof Vest